Shopping Center Loan: Commercial Real Estate Financing Solutions in 2025

Let’s explore Shopping Center Loan: Commercial Real Estate Financing Solutions. Explore financing options for your center loan, including non-recourse commercial mortgages. Refinance today!
Introduction to Shopping Center Financing
Securing financing for shopping center construction is a complex process that requires a strategic approach, detailed planning, and a comprehensive understanding of both the real estate market and the financial instruments available. Shopping centers, being large-scale commercial projects, require significant investment, which is typically sourced through a combination of loans, equity, and other financing mechanisms, often necessitating the involvement of a commercial mortgage broker.
My personal experience with the shopping center loan process
Having been involved in several retail properties projects, I’ve learned firsthand the complexities of securing financing and managing construction. From navigating the intricate process of obtaining construction loans to ensuring the project stays on budget, each phase requires meticulous planning and a deep understanding of both real estate and finance.
My experience has taught me the importance of building strong relationships with lenders who provide retail financing, understanding market trends, and staying adaptable in the face of regulatory challenges. Through careful planning and execution, I’ve successfully guided regional shopping projects from concept to completion, ensuring long-term profitability.
| Section | Main Points |
|---|---|
| Pre-Development Phase | Feasibility studies, land acquisition, permits, and legal fees are crucial for securing a retail shopping center loan. |
| Construction Financing | Short-term loan for building phase; interest-only payments during construction can be particularly beneficial for a strip center project, allowing for better cash flow management. |
| Permanent Financing | Long-term mortgage after construction; usually 20-30 years amortization. |
| Traditional Bank Loans | Requires strong credit history, detailed business plan, substantial collateral. |
| CMBS Loans | Fixed interest rates and non-recourse options are common in conventional shopping center loans, which are also packaged into securities for investors. |
| Mezzanine Financing | Higher risk, higher interest rates, may involve equity participation in a conduit loan program. |
| Joint Ventures and Equity Partnerships | Partners share risks, rewards, expertise, and resources, which can enhance their ability to underwrite larger super-regional shopping center projects effectively. |
| Market Volatility | Economic changes can impact financing terms and project success. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations can increase costs associated with shopping center loans nationwide. |
| Tenant Leasing | Pre-leased spaces and strong tenant mix are essential for securing financing. |
| Feasibility Studies | Critical for assessing project viability and convincing lenders. |
| Refinancing Options | Possible post-construction for better loan terms or additional funds. |
Understanding the Financing Process
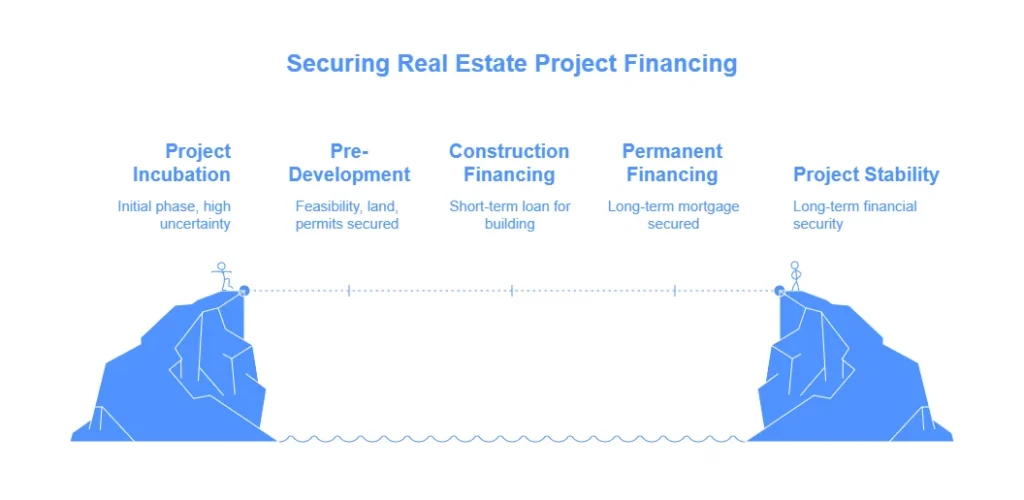
1. Pre-Development Phase
The pre-development phase is critical in laying the foundation for a successful shopping center project. During this phase, developers must conduct feasibility studies, secure land, and obtain the necessary permits. Financing at this stage is often required to cover costs associated with planning, land acquisition, and legal processes.
Key Considerations for financing a super-regional shopping center project include understanding the loan-to-value ratio and potential recourse options.
- Feasibility Studies for a retail center: Essential for assessing the project’s viability, including market demand, competition, and potential revenue streams.
- Land Acquisition: Often requires a significant portion of initial capital.
- Permitting and Legal Fees for shopping center construction loans can be significant. Includes zoning approvals and environmental assessments.
2. Construction Financing
Once the project is deemed viable, the next step is securing shopping center construction loans. This type of financing, particularly shopping center construction loans, is specifically designed to fund the construction phase of the shopping center. It typically involves a short-term loan that is converted into a permanent loan once the construction is completed and the property is stabilized.
Key Elements:
- Loan Structure: Typically, construction loans for competitive shopping centers are structured with interest-only payments during the construction period, with the principal being repaid once the project is completed.
- Interest Rates: Often variable, tied to the prime rate or LIBOR.
- Lender Requirements: Understanding the necessary criteria is essential for securing a conventional shopping loan. Detailed construction plans, budgets, and schedules must be provided to secure financing.

3. Permanent Financing
After the construction is completed, the loan transitions to permanent financing, which is usually a long-term mortgage. This phase is crucial for ensuring the shopping center’s long-term financial stability.
Considerations:
- Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) is a critical metric in commercial real estate financing that lenders assess when providing loans. Lenders typically offer 70-80% LTV, meaning the loan will cover 70-80% of the property’s value.
- Amortization Period for commercial real estate financing typically spans 20-30 years, with fixed or adjustable interest rates. The amortization period usually spans 20-30 years, with fixed or adjustable interest rates that can affect shopping center lending.
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) is a critical metric for assessing the viability of a commercial mortgage for a mall. Lenders often require a DSCR of 1.25 or higher to ensure the property generates sufficient income to cover debt obligations, particularly for a retail shopping center loan.
Types of Financing Options for Shopping Centers
1. Traditional Bank Loans
Traditional bank loans are a common source of financing for shopping centers. These loans, often referred to as commercial real estate loans, are usually provided by commercial banks and require a strong credit history, a detailed business plan, and substantial collateral, often facilitated by a commercial mortgage broker.
2. CMBS Loans
Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities (CMBS) loans are another option, especially for large shopping centers. These business loans for shopping centers are packaged into securities and sold to investors, providing a pool of capital for the lender.
Benefits of securing business loans for shopping centers include increased capital for development and improved cash flow management.
- Fixed Interest Rates: CMBS loans often offer lower fixed interest rates compared to traditional loans.
- Non-recourse financing options are available for certain types of commercial real estate loans, providing additional security for investors. Typically, these loans do not require personal guarantees from the borrower.
3. Mezzanine Financing
Mezzanine financing is a hybrid of debt and equity financing, often used to fill the gap between the primary loan and the total project cost. It is riskier than traditional loans but can provide the necessary capital to complete a project.
Key Features of loans for shopping include fixed interest rates and non-recourse options.
- Higher Interest Rates can impact the overall cost of business loans for shopping centers. Reflect the higher risk associated with mezzanine financing.
- Equity Participation: Lenders may require an equity stake in the project as part of the shopping center lending terms.
4. Joint Ventures and Equity Partnerships
Joint ventures and equity partnerships are common in large-scale shopping center projects. These arrangements involve partnering with investors or other developers to share the risks and rewards of the project.
Advantages:
- Shared Risk: Mitigates individual risk by distributing it across multiple parties.
- Access to expertise in real estate financing is crucial for successful project execution. Partners may bring valuable expertise and resources to the project, enhancing the overall real estate financing strategy.

Key Challenges in Shopping Center Financing
1. Market Volatility
Market conditions can significantly impact the availability and terms of financing for commercial mortgages. Economic downturns, changes in consumer behavior, and shifts in the retail landscape can all affect the success of a shopping center project.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
Navigating the complex regulatory environment is another challenge for those seeking shopping center lending. Developers must comply with a myriad of local, state, and federal regulations, which can delay the project and increase costs.
3. Tenant Leasing and Pre-Sales
Securing tenants and pre-sales is crucial for obtaining favorable financing terms, especially when dealing with mixed-use developments. Lenders are more likely to provide financing if there is a strong tenant mix and a significant portion of the space is pre-leased.
Suggested Diagram: Financing Structure of a Shopping Center Project
A[Shopping Center Project Financing] –> B[Pre-Development Phase]
A –> C[Construction Financing]
A –> D[Permanent Financing]
B --> B1[Feasibility Studies]
B --> B2[Land Acquisition]
B --> B3[Permits & Legal Fees]
C --> C1[Short-Term Loan]
C1 --> C1a[Interest-Only Payments]
C1 --> C1b[Variable Rates: Prime/LIBOR]
C --> C2[Detailed Plans & Budgets]
D --> D1[Long-Term Mortgage]
D1 --> D1a[LTV: 70-80%]
D1 --> D1b[Amortization: 20-30 Years]
D1 --> D1c[DSCR: ≥1.25]
A --> E[Financing Options]
E --> E1[Traditional Bank Loans]
E1 --> E1a[Strong Credit & Collateral]
E --> E2[CMBS Loans]
E2 --> E2a[Fixed Rates]
E2 --> E2b[Non-Recourse]
E --> E3[Mezzanine Financing]
E3 --> E3a[Higher Interest Rates]
E3 --> E3b[Equity Participation]
E --> E4[Joint Ventures/Equity Partnerships]
E4 --> E4a[Shared Risk]
E4 --> E4b[Expertise & Resources]
A --> F[Key Challenges]
F --> F1[Market Volatility]
F --> F2[Regulatory Hurdles]
F --> F3[Tenant Leasing]Related FAQ’s About Shopping Center Financing
1. What is shopping center financing?
Shopping center financing, including loans for shopping centers, refers to the process of securing funds needed to develop, construct, and maintain a shopping center. This can include loans, equity investments, and other financial instruments designed to support each phase of the project.
2. How do I secure a construction loan for a shopping center?
To secure a construction loan, you’ll need a detailed business plan, construction budget, and project timeline. Lenders will also require feasibility studies, land ownership documentation, and proof of permits. It’s important to demonstrate the project’s viability and potential for profitability.
3. What types of loans are available for shopping center projects?
Common types of loans include traditional bank loans, Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities (CMBS) loans, and mezzanine financing. Each option, including shopping center loan rates, has different terms, interest rates, and requirements, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your project’s needs.
4. What is the difference between construction financing and permanent financing?
Construction financing is a short-term loan used to fund the building phase of a shopping center. Once the construction is complete, the loan typically transitions to permanent financing, which is a long-term mortgage designed to be repaid over 20-30 years, anchoring the project’s financial stability.
5. How can joint ventures help in shopping center financing?
Joint ventures allow developers to partner with investors or other developers, sharing the risks and rewards of the project. This can provide additional capital, expertise, and resources, making it easier to secure financing and complete the project.
6. What challenges should I be aware of when financing a shopping center?
Key challenges include market volatility, regulatory hurdles, and securing tenant leases. Economic shifts, changes in consumer behavior, and complex regulations can all impact the success of a shopping center project, especially for retail properties. It’s important to plan for these risks and have contingency plans in place.
7. What role do tenant leases play in securing financing?
Lenders often look for pre-leased spaces or strong tenant commitments when providing financing for anchored and non-anchored shopping projects. A solid tenant mix and signed leases can make your project more attractive to lenders and help you secure better loan terms.
8. Why are feasibility studies important in shopping center financing?
Feasibility studies assess the viability of the shopping center project, considering factors like market demand, competition, and potential revenue. They are crucial for convincing lenders of the project’s profitability and securing the necessary loans for shopping.
9. Can I refinance my shopping center loan?
Feasibility studies assess the viability of the shopping center project, considering factors like market demand, competition, and potential revenue. They are crucial for convincing lenders of the project’s profitability and securing the necessary loans for shopping.
10. How do I choose the right financing option for my shopping center?
Choosing the right financing option for your regional shopping center depends on your project’s specific needs, your financial situation, and market conditions. It’s important to work with financial advisors and lenders who specialize in commercial real estate to find the best solution for your project.
11. What credit score is needed for a commercial loan, especially when lenders assess the risk involved in financing a mixed-use property?
Typically, a credit score of 680 or higher is preferred for a commercial mortgage. However, some lenders may consider scores as low as 620, but you may face higher interest rates or stricter terms.
12. What is the most common form of financing for a small business, and how do various lenders underwrite these loans?
The most common form of financing for small businesses is a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan, like the SBA 7(a) or 504 loan, due to their favorable terms, lower down payments, and flexibility, which help improve cash flow for retailers.
13. How much down payment do you need for a commercial mortgage for a retail center?
Down payments for commercial properties usually range from 10% to 30%, which can vary based on the loan quote provided by lenders. SBA loans may require as little as 10%, while conventional loans often ask for 20-25%, depending on the lender and your financial profile.
14. Do I need a retail commercial loan for a multifamily strip mall?
You may need a retail commercial loan if you’re purchasing, refinancing, or renovating a property for a retail business, like a storefront or shopping center. It depends on your business goals and property needs—consult with a lender to see if a retail shopping center loan fits your situation.
Conclusion
Financing and constructing a shopping center are multifaceted processes that require careful planning, a deep understanding of financial instruments, and the ability to navigate various challenges, particularly in power centers. By leveraging the right financing options and strategies, developers can ensure the successful completion and long-term viability of their mall projects.
share
0 Comments on “Shopping Center Loan: Commercial Real Estate Financing Solutions in 2025”